A successful integration between modeFRONTIER and Lanner's predictive modeling solution, WITNESS, has been featured on the Lanner blog. In the featured case study, Zhendan Xue, Senior Research and Application Engineer at ESTECO North America, presented an example analysis of a test model that has 138 million options. He explained the methodology used to run WITNESS through modeFRONTIER, the algorithms employed and the highly informative charts and tables that result.
"With modeFRONTIER, ESTECO shows that many different and complex objectives can be handled automatically and simultaneously", it is stated in the dedicated Lanner blog post.
The study underlines how process automation and prescriptive analytics can increase the value of simulation and improve decision making. As stated in the study, the key to enhancing the value of simulation lays in the ability to enable predictive and prescriptive analytics on top of the simulation model at hand. To this end, it is crucial to enable a degree of automation, so that the manual effort on behalf of simulation engineers is reduced.
Prescriptive analytics help with acquiring knowledge about the decision space, allowing for an effective identification of optimal solutions. As the foundation of prescriptive analytics, optimization helps identify a set of optimal scenarios that achieve best performance measures. This approach reduces the overall complexity and streamlines the analytics and the decision-making methods applied to simulation, all while reducing the consumption of time and computational efforts.
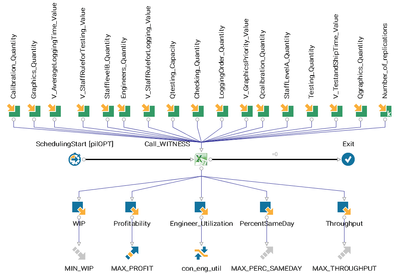
The featured study, explore this aspect of enhancing the value of simulation by integrating a WITNESS Computer Assembly Simulation Model in modeFRONTIER, a comprehensive solution for process automation and optimization in the engineering design process.
The problem at hand is to optimize the assembly line by increasing profitability, total throughput and same-day shipment while minimizing staff utilization, subject to a maximum allowed limit.